Performance Evaluation of Rooftops Rainwater Harvesting Systems (Case Study: City of Sari)

Description
Performance Evaluation of Rooftops Rainwater Harvesting Systems (Case Study: City of Sari)
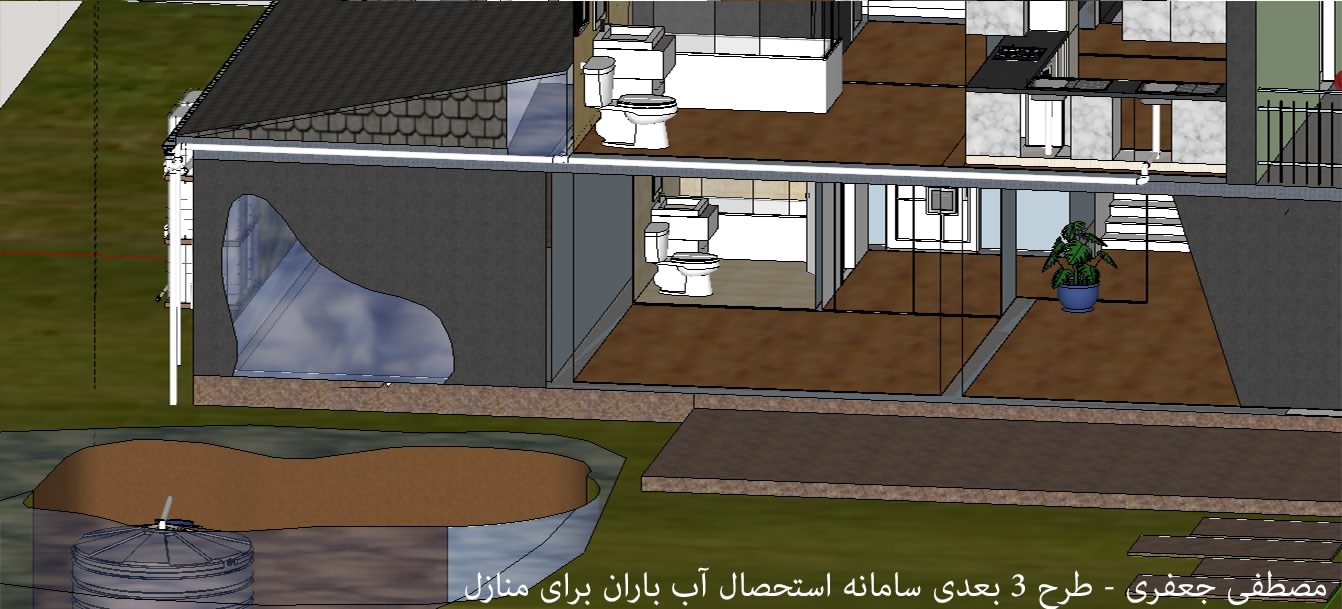
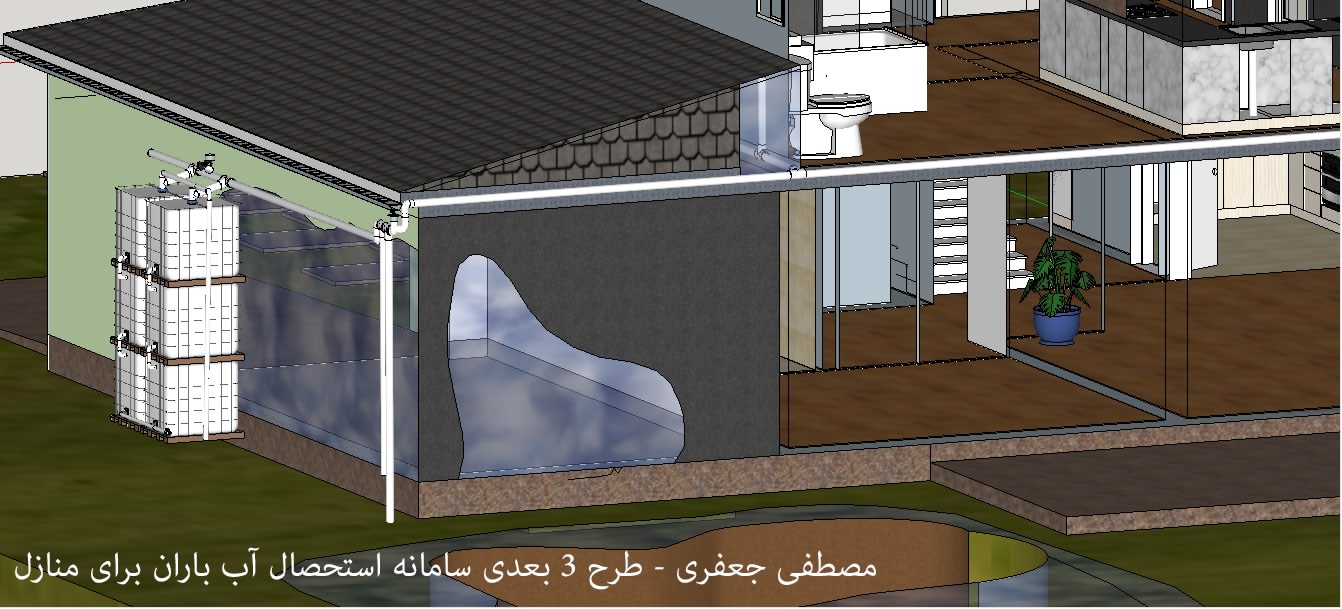
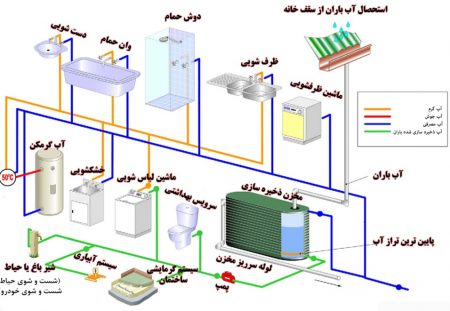
In Iran, water resource management plays a crucial role because it is located in the arid and semi-arid regions. Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is one of the most common traditional techniques for water scarcity problems and domestic consumption in this region for thousands of years. In addition, rainwater can be stored easily in urban areas due to rising urbanization and the growth of impervious surfaces. Rooftop rainwater harvesting (RTRWH) is one of the common methods of rainwater harvesting, and it has lots of advantages.
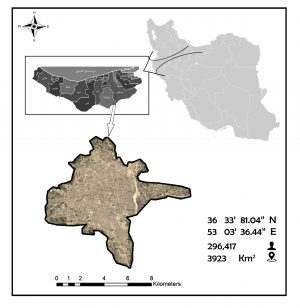
The present research investigates the performance of rooftop rainwater harvesting (RTRWH) systems in Sari, Mazandaran, Iran. The optimal rainwater storage tanks are estimated for four residential houses and a commercial building using 19 years of daily rainfall data (from 1995 to 2015). Accordingly, the mass-curve method was the most suitable method for estimation optimal storage volumes, and the optimal volumes for water reservoirs were 7691, 6768, 11562, 14325, and 18643 (lit/year). The results indicate that using the trial-and-error method is more suitable for buildings that have higher water consumption than annual rainfall.
5th Conference on Rainwater Catchment systems
Authors
M. Jafari Ashourabadi
F. Mojerlou
R. Fazloula